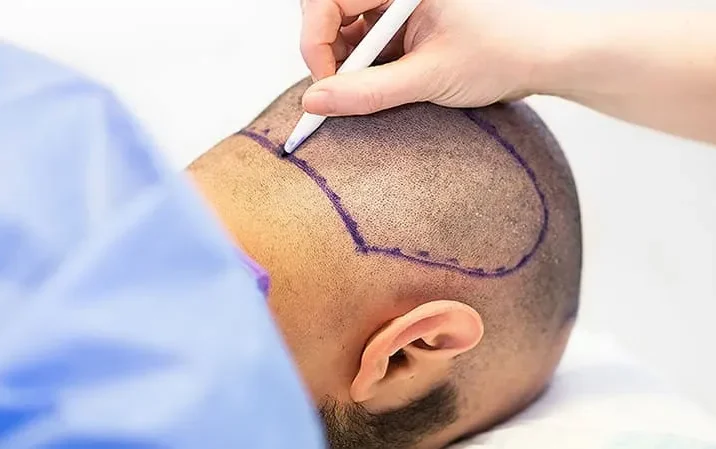
Hair Transplant Donor Area
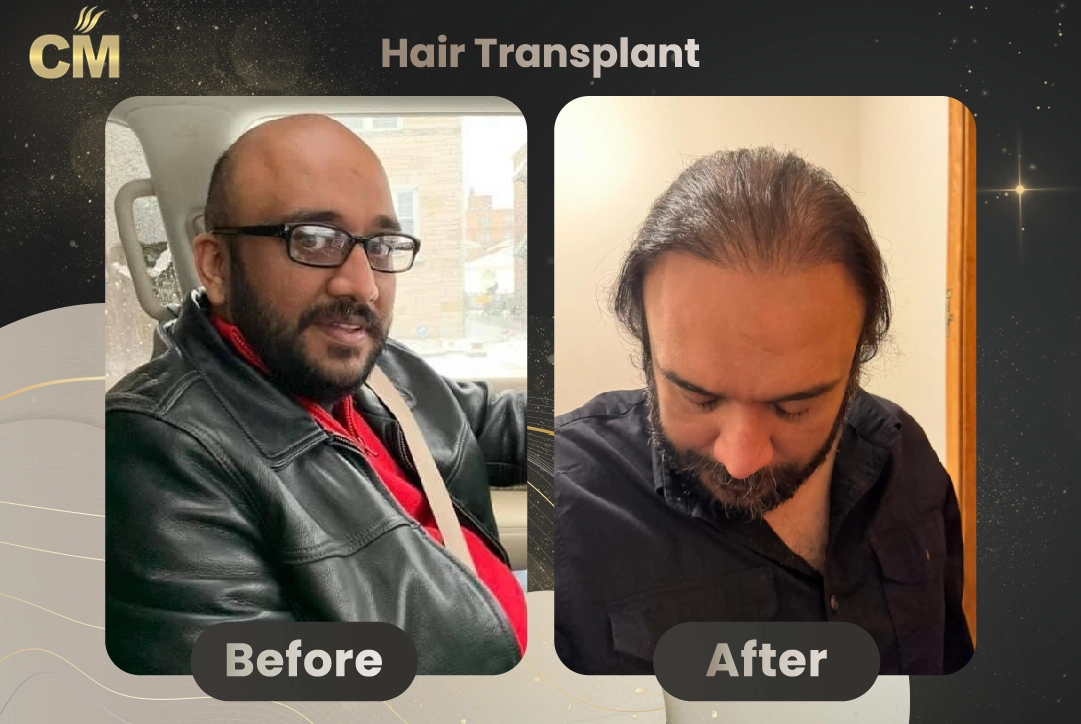
The hair transplant donor area is the foundation of a successful hair restoration procedure. This region, typically located at the back and sides of the scalp, contains hair follicles that are genetically resistant to hair loss. These resilient follicles are harvested and transplanted to thinning or balding areas, ensuring that the new growth is both permanent and natural-looking. Understanding the importance of the donor area is crucial, as its quality and density directly influence the outcome of the transplant, making it a key focus in achieving optimal results.
The Donor Area: Definition and Importance
The Hair Transplant donor area is located at the back of the head, specifically between the ears. It is called the donor area because it provides hair follicles for transplantation and is genetically resistant to baldness. This area is present in all individuals, regardless of hair density, whether large or small.
Why the Donor Area is Ideal for Hair Transplantation
Since the donor area is located on the head, it confirms its suitability for replanting in balding areas, which is a crucial aspect of hair transplantation.
Alternative Donor Areas
In cases where the donor area is weak, other places can be considered for follicle extraction. For instance, the area under the chin can be used, as it is also genetically resistant to baldness and is part of the head.
Common Questions About Alternative Donor Areas
Many people ask if follicles can be extracted from other parts of the body, such as the shoulders, chest, and feet. They often hear from various clinics that this is possible. However, it is essential to understand the limitations of these areas.
Suitability of Alternative Donor Areas
Follicles from areas like the shoulders, chest, and feet are typically weaker and not ideal for transplanting into the head. If used, they might grow for a limited time (up to a year), but they are likely to fall out eventually because they are not genetically resistant to baldness like the hair on the head.
The FUE Technique and the Hair Transplant Donor Area
When to Consider Multiple Hair Transplant Sessions
When discussing the donor area and the FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) technique, it’s important to consider when multiple hair transplant sessions might be necessary.
Calculating the Number of Sessions
The decision on the number of sessions depends on the size and density of the donor and bald areas:
- Large and Dense Donor Area vs. Small or Medium Bald Area:
- If the donor area is large and dense and the bald area is small or medium, typically, one session is sufficient.
- Large and Dense Donor Area vs. Large Bald Area:
- When both the donor area and bald area are large and wide, two sessions may be required to achieve the desired coverage.
- Small and Sparsely Dense Donor Area vs. Small Bald Area:
- If both the donor and bald areas are small, one session is usually enough.
- Small and Sparsely Dense Donor Area vs. Large Bald Area:
- In this scenario, two sessions are often necessary. However, it may not be possible to cover more than 80% of the bald area even after two sessions.
These examples highlight the practical approach to determining the number of hair transplant sessions needed. To avoid a lack of follicles, sometimes follicles from under the chin can be used.
Important Considerations
When extracting follicles from the donor area, it is crucial not to exceed the permissible number to prevent damage to the donor area.
Timing for a Second Hair Transplant Session
After the first session, the donor area needs time to recover, which can take one to two months. The follicles need to heal and reattach, which typically takes 9 to 12 months. Once this period has passed and the follicles have stabilized, a second session can be conducted.
Possibility of a Third Hair Transplant Session
Yes, a third session is possible, but it depends on the strength and capacity of the donor area. The donor area must be able to provide more follicles for further sessions.
Regrowth of Extracted Follicles
Since the follicles are extracted from their roots, they do not grow back in the donor area after extraction.
Hair Color After Transplant
The transplanted follicles retain their original characteristics. If the extracted follicles have white hair, they will grow white hair in the transplanted area as well.
Can I use my brother’s donor area for me?
Even though you and your brother share some genetic similarities, your immune system would still likely recognize his hair follicles as foreign and reject them. This could lead to complications and failure of the transplant. Hair transplants work best when the donor follicles are from the same person. Using follicles from another person, even a close relative, increases the risk of incompatibility and rejection.